When talking about visual perception the most enduring explanation is the Gestalt principles.
Smashing has a good article: https://www.smashingmagazine.com/2014/03/design-principles-visual-perception-and-the-principles-of-gestalt/
Visual Principles (Gestalt):
- Similarity: shapes, color, size
- Continuation: paths, lines, curves, flow
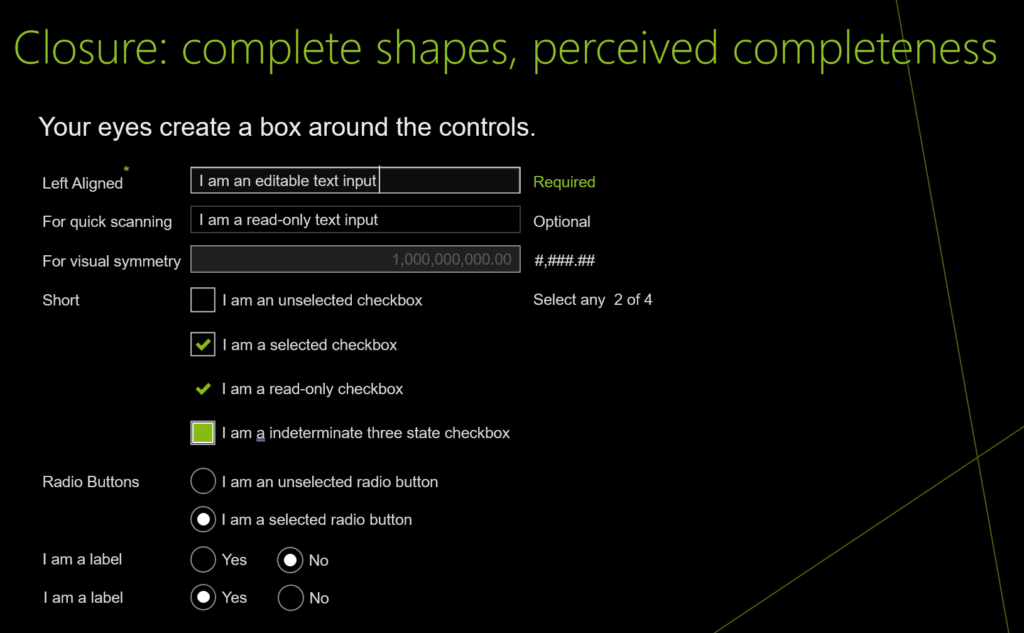
- Closure: complete shapes, perceived completeness
- Proximity: proximity of objects create a perceived larger shape u Figure/ground: visual separation of figures from backgrounds
- Symmetry and order: balanced and complete
Visual Principles (Gestalt) examples:
Similarity: shapes, color, size

Continuation: paths, lines, curves, flow

Closure: complete shapes, perceived completeness

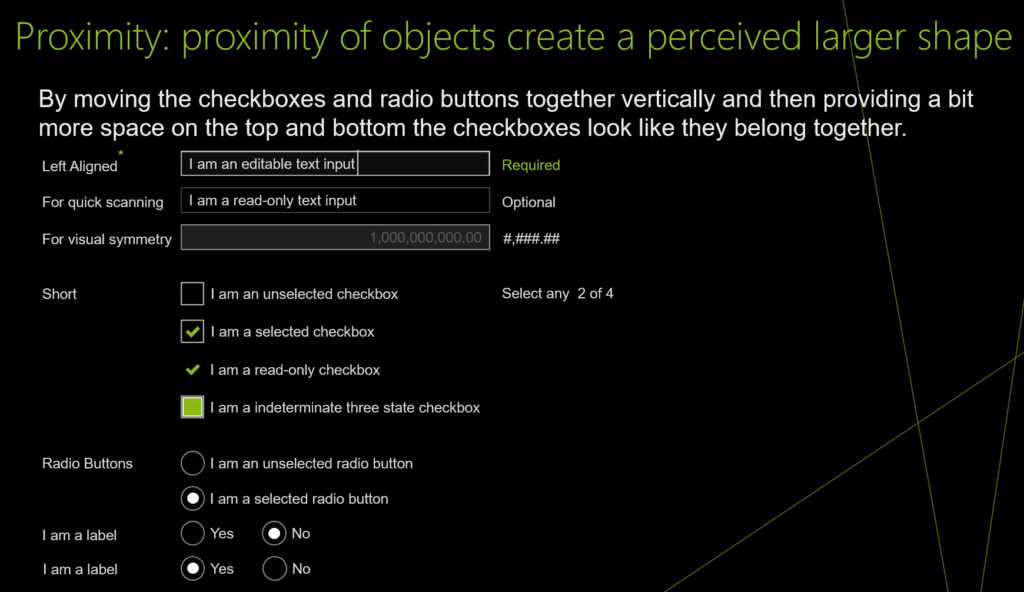
Proximity: proximity of objects create a perceived larger shape
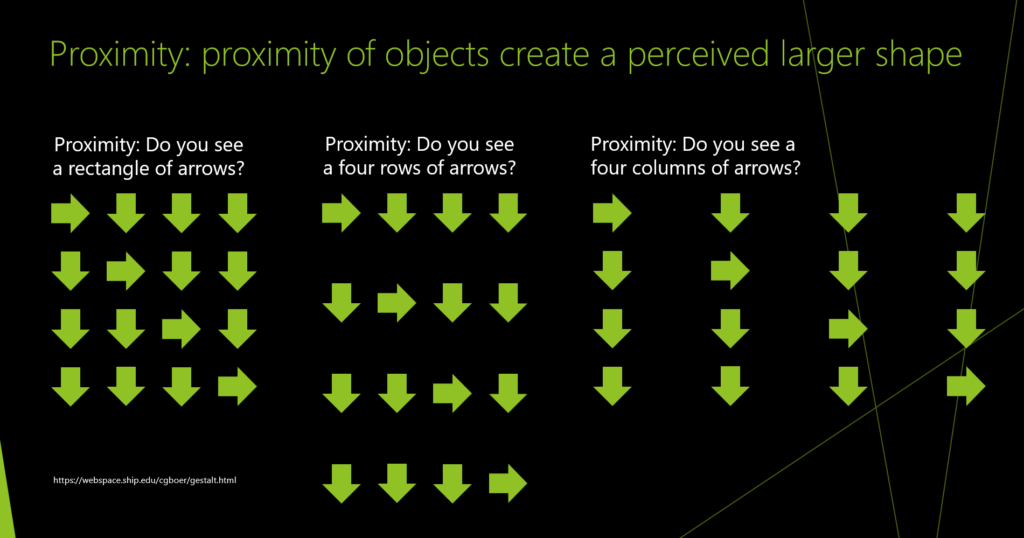
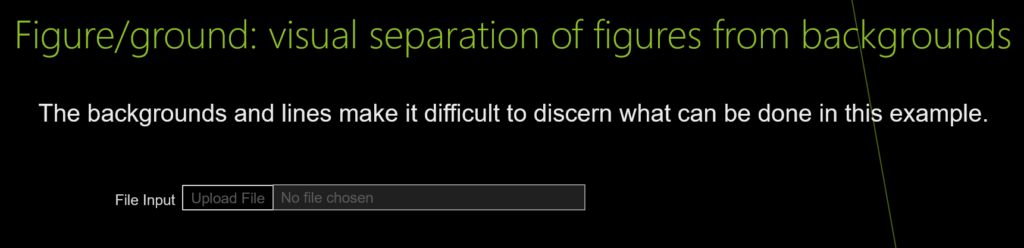
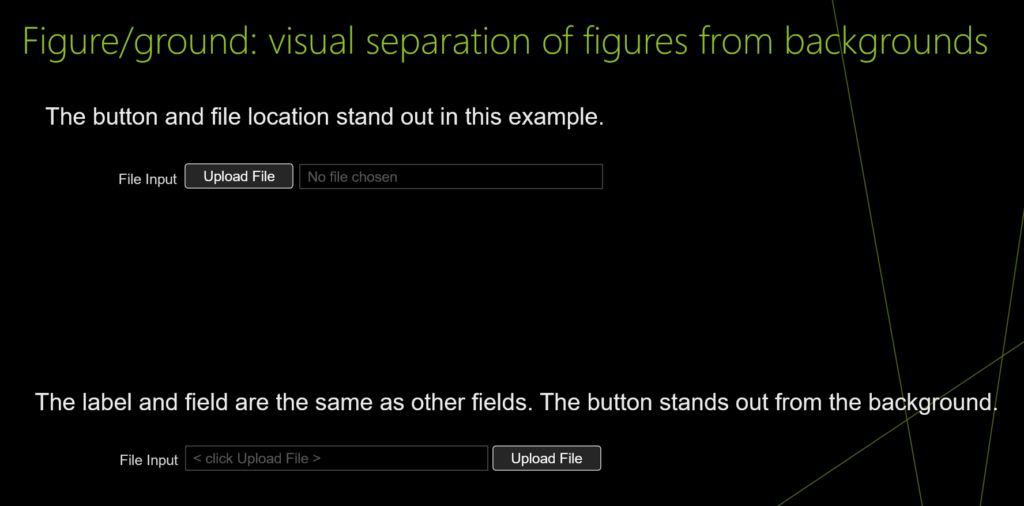
Figure/ground: visual separation of figures from backgrounds

Symmetry and order: balanced and complete

Deeper Dive: Video explainers
- Gestalt Principles. How psychology influences your design strategy. – by Art with Kunstler
- Gestalt Psychology and Why It’s Essential for Good Design – by HubSpot Marketing
Deeper Dive: Further reading
- https://webspace.ship.edu/cgboer/gestalt.html
- https://www.smashingmagazine.com/2014/03/design-principles-visual-perception-and-the-principles-of-gestalt/
- https://www.interaction-design.org/literature/topics/gestalt-principles
- https://lawsofux.com/
Apply what you have learned to UI Design and Development following the above rules.
UI design and development example for Similarity: shapes, color, size
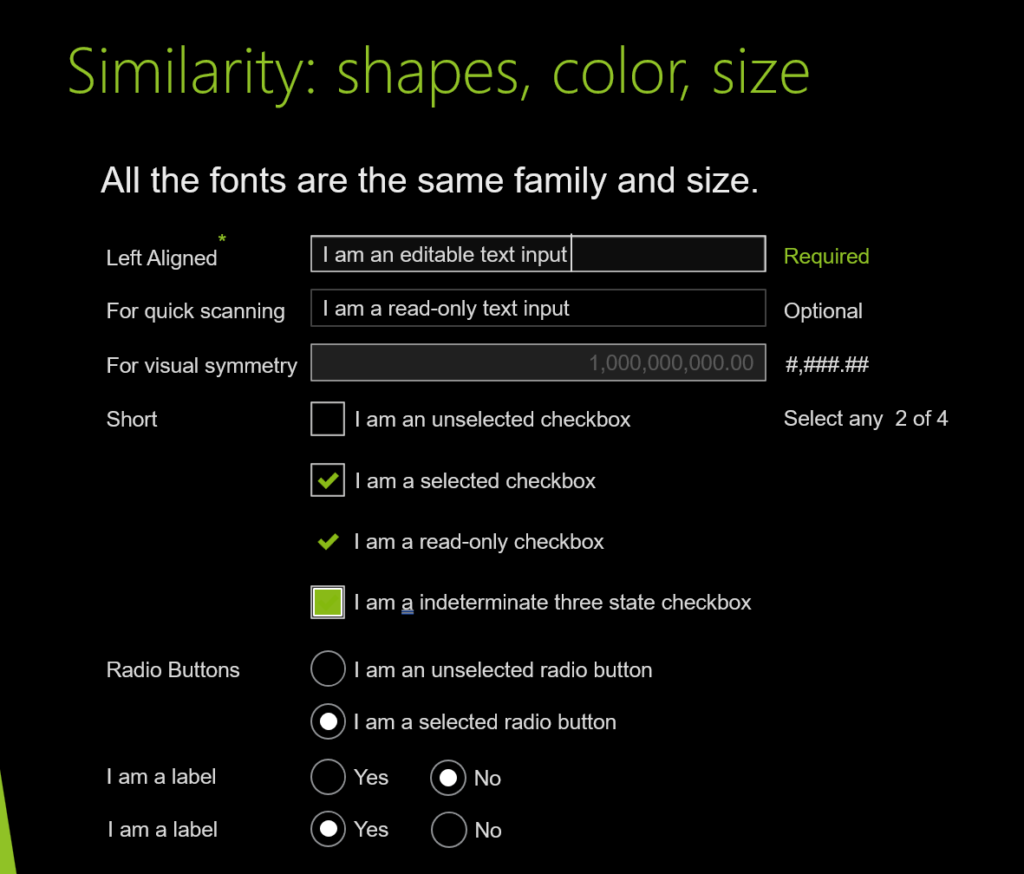
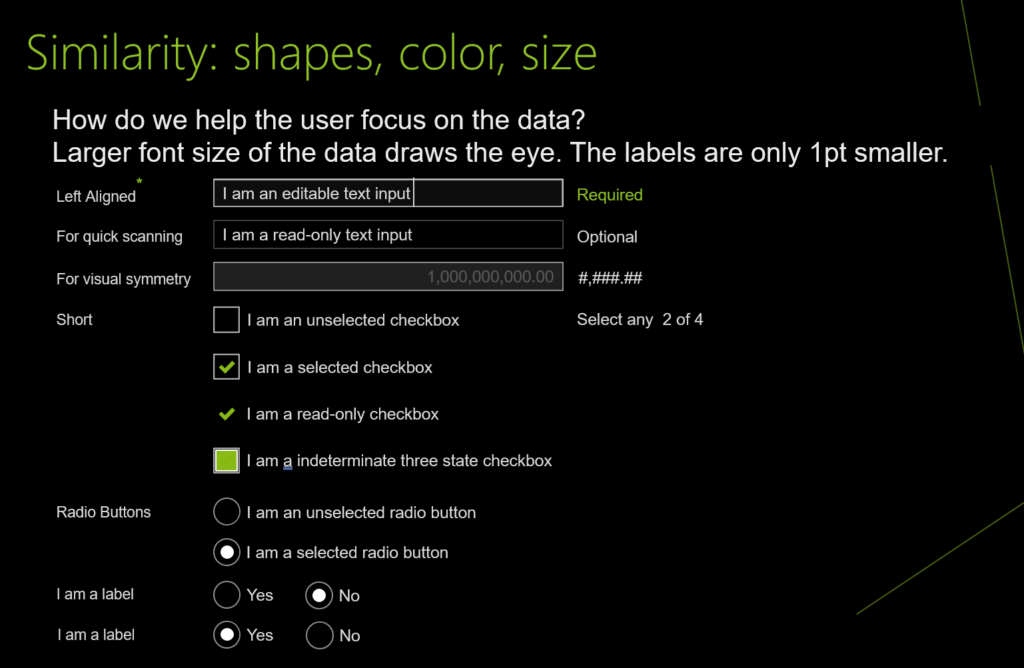
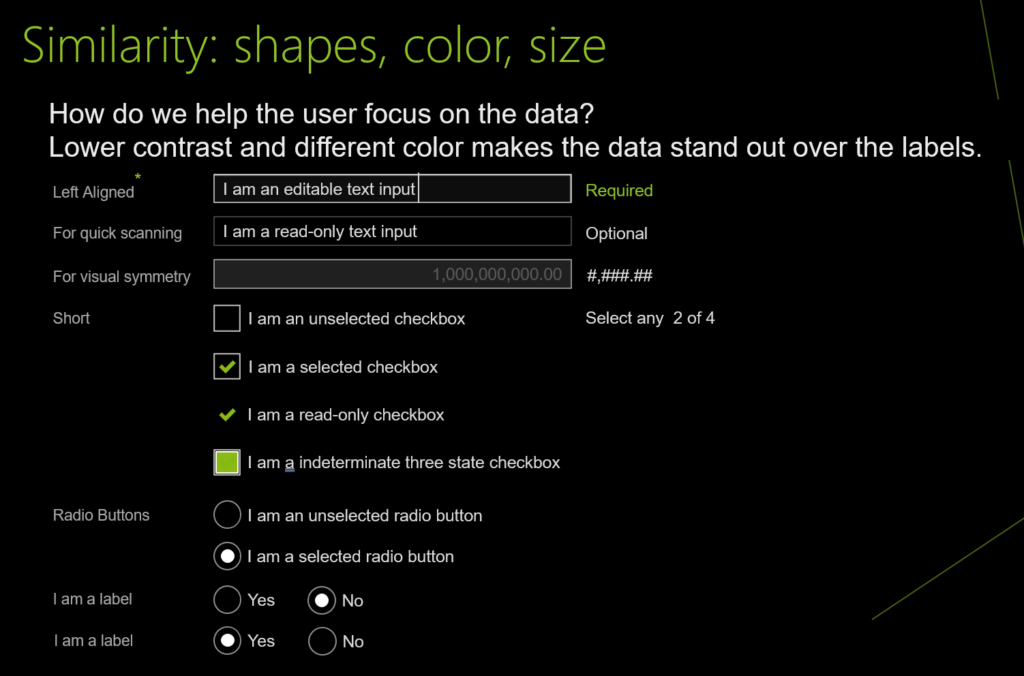
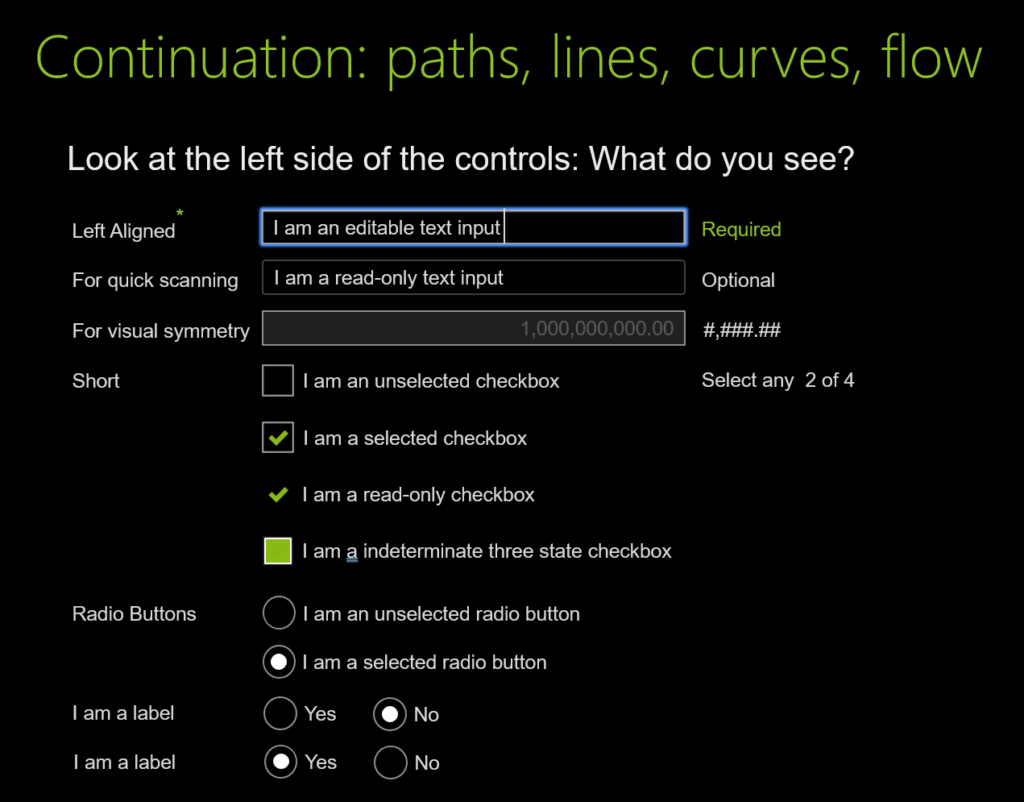
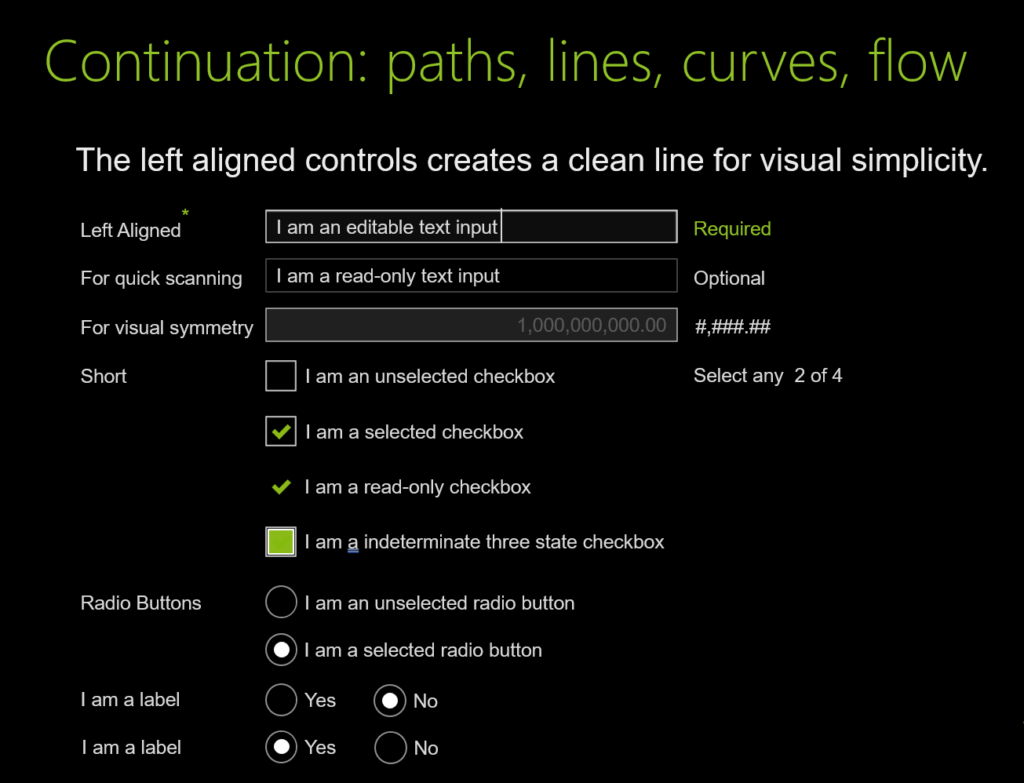
UI design and development example for Continuation: paths, lines, curves, flow

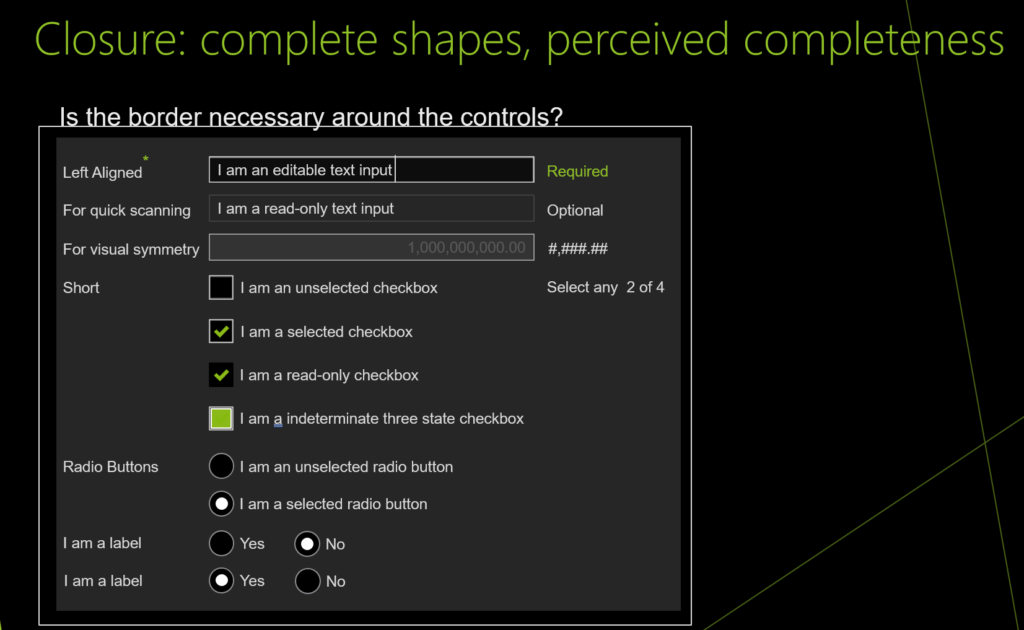
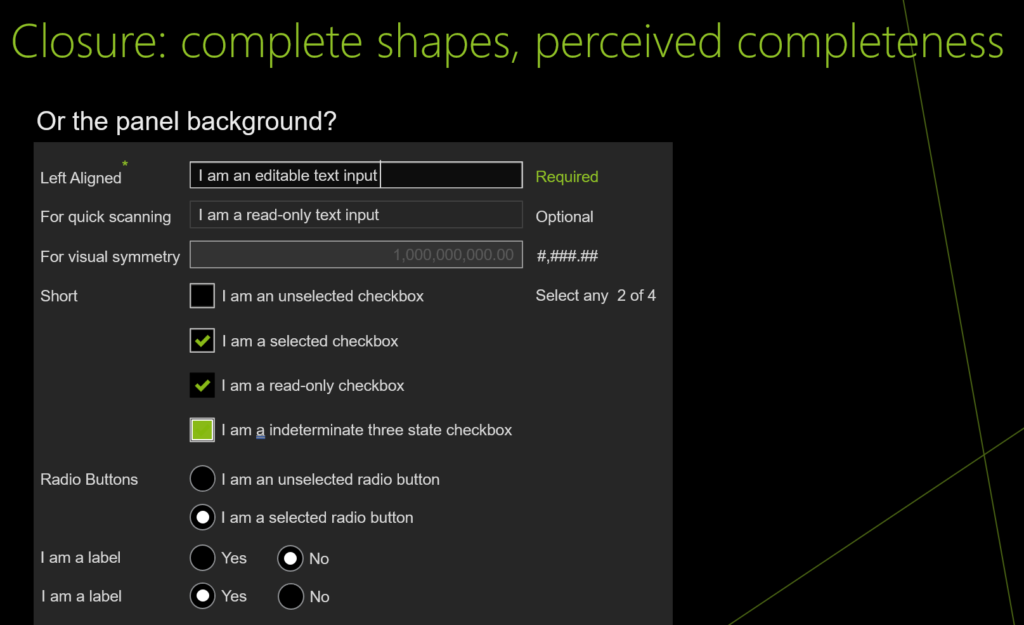
UI design and development example for Closure: complete shapes, perceived completeness
UI design and development example for Proximity: proximity of objects create a perceived larger shape

UI design and development example for Figure/ground: visual separation of figures from backgrounds
UI design and development example for Symmetry and order: balanced and complete
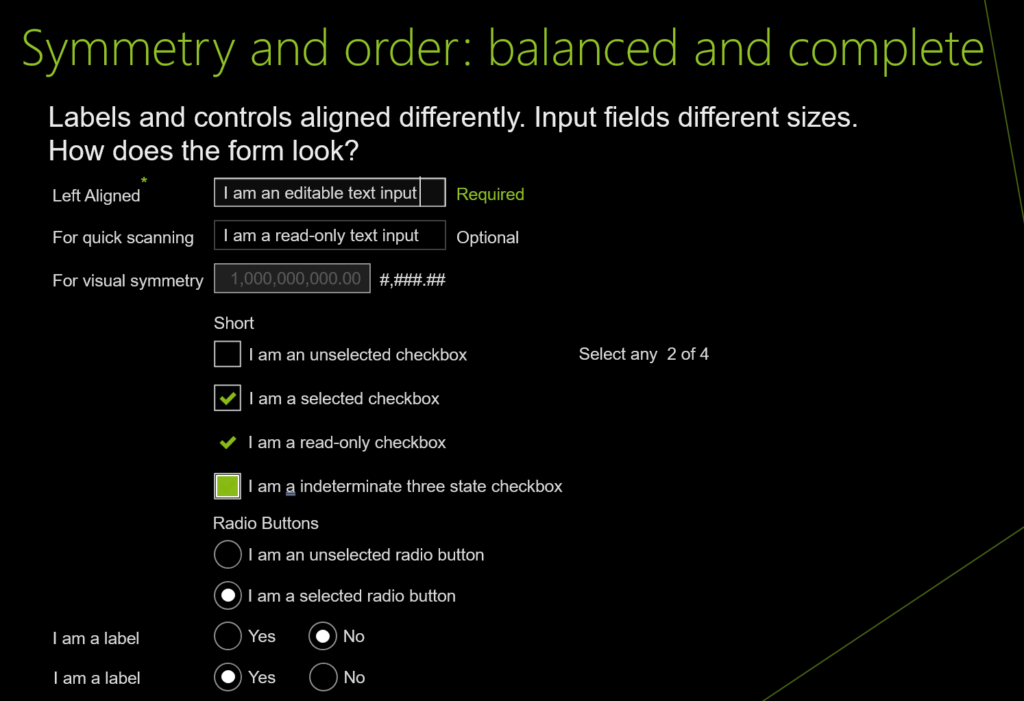
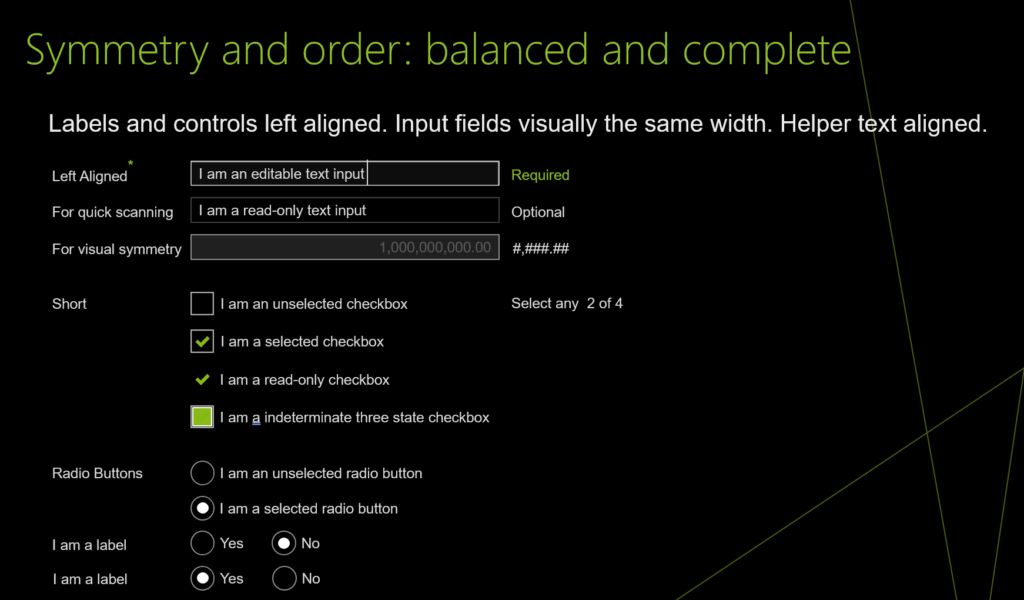
As you work on the UIs for your products, ponder the following:
- For many developers the view is inside out. There are many objects to be placed on the screen and they need to function properly so the application works.
- For many designers the view is outside in. There are many objects to be placed on the screen so that it makes in simpler for the user to get their tasks accomplished.
The following can help the designer and developer get on the same page
- Similarity: shapes, color, size
- Continuation: paths, lines, curves, flow
- Closure: complete shapes, perceived completeness
- Proximity: proximity of objects create a perceived larger shape
- Figure/ground: visual separation of figures from backgrounds Symmetry and order: balanced and complete
